Під час бойових дій надзвичайно важливо забезпечити бійців обладнанням для виявлення та ідентифікації, таким як тепловізори та прилади нічного бачення (ПНБ). Багато хто помилково вважає, що це одне й те саме, однак насправді можливості цих приладів суттєво відрізняються.
У цій статті ми детально розберемо принцип роботи кожного приладу, їхні переваги та недоліки, наведемо думки експертів і перевірені факти. У результаті ви дізнаєтеся, що краще – тепловізор чи прилад нічного бачення – залежно від ваших завдань, будь то військові операції, полювання чи охорона периметра, і як обрати оптимальний пристрій.
We will explain the nuances in simple language, with references to authoritative sources, and provide recommendations on how to choose.
Під час бойових дій надзвичайно важливо забезпечити бійців обладнанням для виявлення та ідентифікації, таким як тепловізори та прилади нічного бачення (ПНБ). Багато хто помилково вважає, що це одне й те саме, однак насправді можливості цих приладів суттєво відрізняються.
У цій статті ми детально розберемо принцип роботи кожного приладу, їхні переваги та недоліки, наведемо думки експертів і перевірені факти. У результаті ви дізнаєтеся, що краще – тепловізор чи прилад нічного бачення – залежно від ваших завдань, будь то військові операції, полювання чи охорона периметра, і як обрати оптимальний пристрій.
We will explain the nuances in simple language, with references to authoritative sources, and provide recommendations on how to choose.
Contents
- How night vision devices (NVDs) work
- Types of night vision devices
- How a thermal imager works
- Types of thermal imagers
- Advantages and disadvantages of night vision devices
- Advantages and disadvantages of thermal imagers
- What to choose: a thermal imager or a night vision device?
- Conclusion and recommendations of experts
Contents
- How night vision devices (NVDs) work
- Types of night vision devices
- How a thermal imager works
- Types of thermal imagers
- Advantages and disadvantages of night vision devices
- Advantages and disadvantages of thermal imagers
- What to choose: a thermal imager or a night vision device?
- Conclusion and recommendations of experts
How does a night vision device (NVD) work?
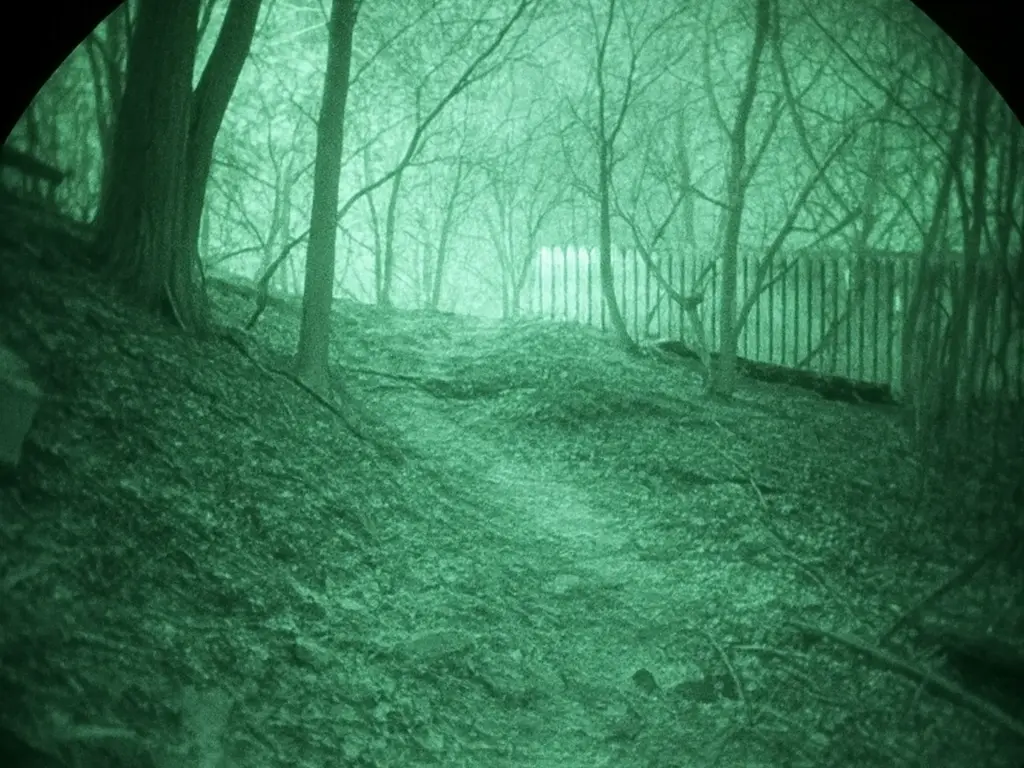
A night vision device is designed to amplify the faint available light and convert it into a visible image. In simple terms, an NVD captures residual light —such as starlight, moonlight, or infrared (IR) illumination — and amplifies it many times over, allowing you to "see" in the dark.
У класичних аналого-оптичних ПНБ це досягається за допомогою електронно-оптичного перетворювача (ЕОП): об’єктив збирає слабке світло, фотокатод перетворює фотони на електрони, потік електронів підсилюється і висвічує зображення на люмінофорному екрані (як правило, зеленуватого кольору). Такий зелений відтінок добре знайомий з військових фільмів і зумовлений особливостями люмінофора.
Сучасні цифрові ПНБ працюють подібним чином, але замість ЕОП використовують чутливу CMOS-матрицю; підсилюючи сигнали, пристрій виводить картинку на вбудований дисплей. За нестачі природного світла багато ПНБ оснащуються ІЧ-іллюмінатором – невидимим інфрачервоним ліхтарем. Він підсвічує ціль ІЧ-світлом, яке вловлюється приладом, хоча є невидимим для ока, тим самим дозволяючи бачити навіть у повній темряві.
A typical image through a night vision device – the scene is illuminated only by stars and IR illumination, forming a greenish monochrome image.
How does a night vision device (NVD) work?
A night vision device is designed to amplify the faint available light and convert it into a visible image. In simple terms, an NVD captures residual light —such as starlight, moonlight, or infrared (IR) illumination — and amplifies it many times over, allowing you to "see" in the dark.
У класичних аналого-оптичних ПНБ це досягається за допомогою електронно-оптичного перетворювача (ЕОП): об’єктив збирає слабке світло, фотокатод перетворює фотони на електрони, потік електронів підсилюється і висвічує зображення на люмінофорному екрані (як правило, зеленуватого кольору). Такий зелений відтінок добре знайомий з військових фільмів і зумовлений особливостями люмінофора.
Сучасні цифрові ПНБ працюють подібним чином, але замість ЕОП використовують чутливу CMOS-матрицю; підсилюючи сигнали, пристрій виводить картинку на вбудований дисплей. За нестачі природного світла багато ПНБ оснащуються ІЧ-іллюмінатором – невидимим інфрачервоним ліхтарем. Він підсвічує ціль ІЧ-світлом, яке вловлюється приладом, хоча є невидимим для ока, тим самим дозволяючи бачити навіть у повній темряві.
A typical image through a night vision device – the scene is illuminated only by stars and IR illumination, forming a greenish monochrome image.

Types of night vision devices
There are several types of night vision devices (NVDs) designed for different purposes:
- Monoculars are devices with a single eyepiece. They are lightweight and compact, convenient for hiking, camping, and situations where mobility is important. A monocular can be quickly raised to the eye for brief observation.
- Binoculars are devices with two eyepieces. They provide a wider field of view and a stereoscopic effect, which is useful for hunting, reconnaissance, or even combat. The binocular format reduces eye strain during prolonged observation.
- Night sights or sight attachments are mounted on weapons for aiming in the dark. These devices enable accurate shooting at night. They are used by both hunters and military snipers.
Варто зазначити, що ефективність будь-якого ПНБ залежить від наявності хоча б мінімального джерела світла – наприклад, зоряного неба або далекого ліхтаря. В абсолютній темряві без ІЧ-підсвічування жоден прилад нічного бачення не працює. Крім того, старі покоління аналогових ПНБ були вразливими до яскравих спалахів світла: різке освітлення могло тимчасово засліпити користувача або навіть вивести з ладу ЕОП. У сучасних моделях цю проблему вирішено – при появі осліплювального спалаху пристрій автоматично знижує підсилення або вимикається.
Types of night vision devices
There are several types of night vision devices (NVDs) designed for different purposes:
- Monoculars are devices with a single eyepiece. They are lightweight and compact, convenient for hiking, camping, and situations where mobility is important. A monocular can be quickly raised to the eye for brief observation.
- Binoculars are devices with two eyepieces. They provide a wider field of view and a stereoscopic effect, which is useful for hunting, reconnaissance, or even combat. The binocular format reduces eye strain during prolonged observation.
- Night sights or sight attachments are mounted on weapons for aiming in the dark. These devices enable accurate shooting at night. They are used by both hunters and military snipers.
Варто зазначити, що ефективність будь-якого ПНБ залежить від наявності хоча б мінімального джерела світла – наприклад, зоряного неба або далекого ліхтаря. В абсолютній темряві без ІЧ-підсвічування жоден прилад нічного бачення не працює. Крім того, старі покоління аналогових ПНБ були вразливими до яскравих спалахів світла: різке освітлення могло тимчасово засліпити користувача або навіть вивести з ладу ЕОП. У сучасних моделях цю проблему вирішено – при появі осліплювального спалаху пристрій автоматично знижує підсилення або вимикається.
How does a thermal imager work?
A thermal imager is a device that "sees" heat. Unlike night vision devices (NVDs), which respond to reflected light rays, a thermal imager registers the infrared (thermal) radiation of objects. Any body with a temperature above absolute zero emits heat that is invisible to the eye but detectable by thermal sensors.
Принцип роботи тепловізора ґрунтується на технології інфрачервоної термографії: спеціальний мікроболометричний датчик (матриця з тисяч чутливих елементів) фіксує довгохвильове ІЧ-випромінювання від об’єктів, розрізняючи навіть мінімальні перепади температури. Далі вбудований процесор перетворює дані датчика у температурну карту і створює зображення, де більш гарячі зони виділяються контрастніше на тлі холодніших. У результаті на екрані формується характерна теплова картина — теплі об’єкти відображаються яскравими (наприклад, білими або червоними) плямами, а холодні — темними (чорними, синіми тощо).
Такий прилад не потребує жодного зовнішнього освітлення: тепловізор здатен працювати у повній темряві, в умовах димки, туману чи запиленості — там, де звичайна камера або ПНБ вже безсилі. Як зазначає виробник FLIR, на відміну від пристроїв, що залежать від відбитого світла, тепловізори однаково добре «бачать» і вдень, і вночі, формуючи контрастну картинку завдяки власному тепловому сигналу. Саме тому тепловізори вважаються найкращим рішенням для цілодобового спостереження у складних умовах.
Відмінною особливістю тепловізорів є їхні об’єктиви: звичайне скло не пропускає дальній інфрачервоний діапазон, тому лінзи тепловізійних приладів виготовляють зі спеціальних матеріалів — германію, селеніду цинку або халькогенідного скла. Ці матеріали прозорі для теплових хвиль, але не пропускають видиме світло, тобто працюють прямо навпаки звичайної оптики. Тепловізійна оптика дорожча і важча за скляну, проте дозволяє приладу фокусувати випромінювання об’єктів і «бачити» їхній тепловий образ.
Усередині тепловізор зазвичай містить: об’єктив, мікроболометр (тепловий сенсор), електронну частину для обробки сигналу та екран для відображення зображення.
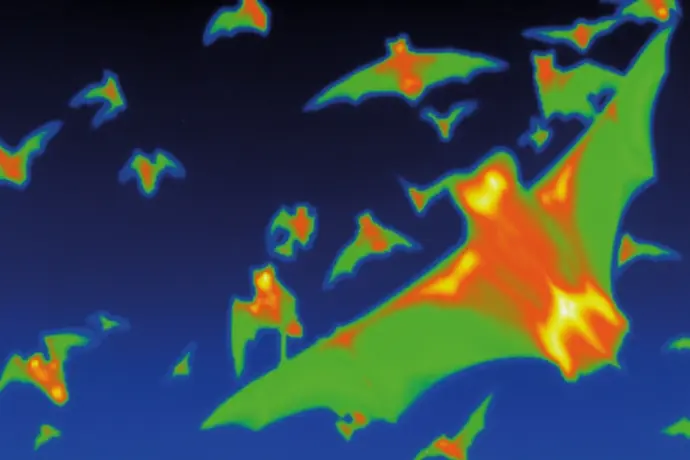
Thermal imagers visualize temperature distribution. The thermal image of flying mice clearly shows that the heat of their bodies stands out brightly against the colder background (FLIR camera image).
How does a thermal imager work?
A thermal imager is a device that "sees" heat. Unlike night vision devices (NVDs), which respond to reflected light rays, a thermal imager registers the infrared (thermal) radiation of objects. Any body with a temperature above absolute zero emits heat that is invisible to the eye but detectable by thermal sensors.
Принцип роботи тепловізора ґрунтується на технології інфрачервоної термографії: спеціальний мікроболометричний датчик (матриця з тисяч чутливих елементів) фіксує довгохвильове ІЧ-випромінювання від об’єктів, розрізняючи навіть мінімальні перепади температури. Далі вбудований процесор перетворює дані датчика у температурну карту і створює зображення, де більш гарячі зони виділяються контрастніше на тлі холодніших. У результаті на екрані формується характерна теплова картина — теплі об’єкти відображаються яскравими (наприклад, білими або червоними) плямами, а холодні — темними (чорними, синіми тощо).
Такий прилад не потребує жодного зовнішнього освітлення: тепловізор здатен працювати у повній темряві, в умовах димки, туману чи запиленості — там, де звичайна камера або ПНБ вже безсилі. Як зазначає виробник FLIR, на відміну від пристроїв, що залежать від відбитого світла, тепловізори однаково добре «бачать» і вдень, і вночі, формуючи контрастну картинку завдяки власному тепловому сигналу. Саме тому тепловізори вважаються найкращим рішенням для цілодобового спостереження у складних умовах.
Відмінною особливістю тепловізорів є їхні об’єктиви: звичайне скло не пропускає дальній інфрачервоний діапазон, тому лінзи тепловізійних приладів виготовляють зі спеціальних матеріалів — германію, селеніду цинку або халькогенідного скла. Ці матеріали прозорі для теплових хвиль, але не пропускають видиме світло, тобто працюють прямо навпаки звичайної оптики. Тепловізійна оптика дорожча і важча за скляну, проте дозволяє приладу фокусувати випромінювання об’єктів і «бачити» їхній тепловий образ.
Усередині тепловізор зазвичай містить: об’єктив, мікроболометр (тепловий сенсор), електронну частину для обробки сигналу та екран для відображення зображення.
Thermal imagers visualize temperature distribution. The thermal image of flying mice clearly shows that the heat of their bodies stands out brightly against the colder background (FLIR camera image).
Types of thermal imagers
Similar to night vision devices (NVDs), thermal imaging devices come in several types:
- Thermal imaging monoculars are compact and lightweight "tubes" designed to be carried in the hand. They are convenient to quickly raise to the eye for surveying the terrain. Despite their small size, modern monoculars allow you to see in complete darkness at considerable distances. For example, some models are capable of detecting a person at a distance of over 2.5 km. Monoculars are popular among infantry and hunters for scanning the terrain.
- Thermal imaging binoculars are systems that usually have two eyepieces (sometimes with two lenses) that create a stereoscopic image. They provide a wider field of view and comfort during prolonged observation by engaging both eyes. Such binoculars allow you to spot targets in the dark at long distances, which is valuable for reconnaissance, border patrol, or rescue operations.
- Thermal imaging sights are sights for weapons equipped with a thermal sensor. They are designed for accurate shooting at night, allowing the shooter to see the target even through light smoke, fog, or through bushes. Thermal imaging sights are indispensable for snipers and hunters who want to shoot in complete darkness. Many modern thermal sights are equipped with rangefinders, ballistic calculators, and other features.
- Thermal imaging attachments are special modular thermal imagers that can be mounted on the lens of a daytime optical sight, turning it into a thermal sight. These attachments allow you to quickly convert your existing optics for nighttime use. This is convenient for shooters who need to use their sights flexibly in different conditions.
Тепловізори сьогодні застосовуються повсюдно: від військової справи та полювання до будівельної діагностики і енергетики. Вони дозволяють виявляти тепловтрати у будівлях, перегрів проводки, здійснювати пошуково-рятувальні роботи (шукати людей під завалами за їхнім теплом) та багато іншого. У військових умовах тепловізори цінуються за здатність виявляти замасковані цілі — живих істот або техніку — за їхнім тепловим слідом практично за будь-яких умов освітленості й у будь-який час доби.
Втім, варто розуміти і обмеження: оптика тепловізора не бачить крізь скло. Наприклад, дивлячись тепловізором у вікно автомобіля, ви не побачите нічого, окрім власного відображення, оскільки скло блокує тепло від зовнішніх об’єктів. Крім того, хоча тепловізор не залежить від видимого світла, сильні перешкоди у вигляді щільних перепон можуть знизити його ефективність. Так, зливний дощ або мокрий сніг заважають роботі як тепловізора, так і ПНБ — потоки води екранують випромінювання об’єктів. Так само, якщо температура навколишнього середовища вирівнялася (наприклад, у спеку, коли і об’єкт, і фон нагрілися до схожої температури), контраст теплового зображення знижується. Добре замаскований противник може зменшити своє теплове поле (наприклад, накрившись теплоізоляційним матеріалом), і тоді виявити його буде складніше. Попри це, у більшості нічних ситуацій тепловізор дає значно більше шансів помітити ціль, ніж звичайна камера або ПНБ.
Types of thermal imagers
Similar to night vision devices (NVDs), thermal imaging devices come in several types:
- Thermal imaging monoculars are compact and lightweight "tubes" designed to be carried in the hand. They are convenient to quickly raise to the eye for surveying the terrain. Despite their small size, modern monoculars allow you to see in complete darkness at considerable distances. For example, some models are capable of detecting a person at a distance of over 2.5 km. Monoculars are popular among infantry and hunters for scanning the terrain.
- Thermal imaging binoculars are systems that usually have two eyepieces (sometimes with two lenses) that create a stereoscopic image. They provide a wider field of view and comfort during prolonged observation by engaging both eyes. Such binoculars allow you to spot targets in the dark at long distances, which is valuable for reconnaissance, border patrol, or rescue operations.
- Thermal imaging sights are sights for weapons equipped with a thermal sensor. They are designed for accurate shooting at night, allowing the shooter to see the target even through light smoke, fog, or through bushes. Thermal imaging sights are indispensable for snipers and hunters who want to shoot in complete darkness. Many modern thermal sights are equipped with rangefinders, ballistic calculators, and other features.
- Thermal imaging attachments are special modular thermal imagers that can be mounted on the lens of a daytime optical sight, turning it into a thermal sight. These attachments allow you to quickly convert your existing optics for nighttime use. This is convenient for shooters who need to use their sights flexibly in different conditions.
Тепловізори сьогодні застосовуються повсюдно: від військової справи та полювання до будівельної діагностики і енергетики. Вони дозволяють виявляти тепловтрати у будівлях, перегрів проводки, здійснювати пошуково-рятувальні роботи (шукати людей під завалами за їхнім теплом) та багато іншого. У військових умовах тепловізори цінуються за здатність виявляти замасковані цілі — живих істот або техніку — за їхнім тепловим слідом практично за будь-яких умов освітленості й у будь-який час доби.
Втім, варто розуміти і обмеження: оптика тепловізора не бачить крізь скло. Наприклад, дивлячись тепловізором у вікно автомобіля, ви не побачите нічого, окрім власного відображення, оскільки скло блокує тепло від зовнішніх об’єктів. Крім того, хоча тепловізор не залежить від видимого світла, сильні перешкоди у вигляді щільних перепон можуть знизити його ефективність. Так, зливний дощ або мокрий сніг заважають роботі як тепловізора, так і ПНБ — потоки води екранують випромінювання об’єктів. Так само, якщо температура навколишнього середовища вирівнялася (наприклад, у спеку, коли і об’єкт, і фон нагрілися до схожої температури), контраст теплового зображення знижується. Добре замаскований противник може зменшити своє теплове поле (наприклад, накрившись теплоізоляційним матеріалом), і тоді виявити його буде складніше. Попри це, у більшості нічних ситуацій тепловізор дає значно більше шансів помітити ціль, ніж звичайна камера або ПНБ.
Advantages and disadvantages of night vision devices and thermal imagers
Let's consider the strengths and weaknesses of each type of device. Below is a comparative summary based on expert data.
Advantages and disadvantages of night vision devices (NVD)
Advantages:
- High image detail. PNBs display objects as they are, but only in low light conditions. Newer generation devices provide a clear picture—you can distinguish faces, inscriptions, and small details. This is critical if you need to recognize a person or read a map in the dark.
- Natural perception of the scene. The image through the night vision device is close to what the eye sees in sufficient lighting (monochrome only). This makes it easier to navigate the terrain—you can see the relief, obstacles, and objects in their usual perspective. For example, when driving at night, soldiers use night vision goggles, which allow them to see the road and the surrounding terrain in its natural form.
- Effective operation in low light conditions. Even very faint light from stars or distant sources is sufficient for a high-quality PNB to form an image. With a third-generation device, you can observe on a moonless night—the starry sky and atmospheric glow often provide the necessary background. And with an IR illuminator, the PNB works even in complete darkness.
- Відносно невисока вартість. Класичні ПНБ і цифрові пристрої нічного бачення зазвичай дешевші за тепловізори аналогічного класу. Технологія підсилення видимого світла відпрацьована десятиліттями, виробництво ЕОП (особливо Gen 1–2) налагоджене, тому базові моделі доступні за ціною. Багато користувачів обирають ПНБ саме через бюджетні обмеження — нічні прилади можуть коштувати у кілька разів дешевше за тепловізори аналогічного призначення. Наприклад, найпростіший тепловізійний монокуляр обійдеться як два прилади нічного бачення 1-го покоління. Якщо бюджет обмежений — ПНБ часто є єдиним варіантом отримати пристрій для нічного полювання чи охорони.
Disadvantages:
- Complete darkness is the enemy of night vision devices. Without any external light (or without active IR illumination), a night vision device is useless. It cannot "see" anything if it is completely dark around it — this is a fundamental limitation of night vision devices. In addition, an IR illuminator, although invisible to the eye, can expose the observer if the enemy also has NVG.
- Чутливість до погодних умов. Для нормальної роботи ПНБ потрібен хоча б слабкий, але прямий огляд цілі. Дим, туман, пил або сильний дощ істотно погіршують якість зображення або роблять його неможливим. У густому тумані чи заметілі нічник стає безкорисним — світло розсіюється, не доходячи до приладу. Також у заростях чи за укриттями нерухому ціль із ПНБ можна просто не помітити. У таких випадках тепловізор, який бачить тепло крізь перешкоди, має величезну перевагу.
- The danger of bright light. Despite the presence of protection, flashes of bright light (e.g., headlights or explosions) can still temporarily blind the PNB user and overload the device's matrix. Older analog devices may even fail (burn out the image intensifier tube) when exposed to a sudden flash. Digital models are more reliable in this regard, but their sensitivity is also limited by the dynamic range of the sensor.
- Limited detection range. Although night vision devices allow you to see details better, the distance at which you can spot a target is limited by their ability to collect scattered light. Night vision devices are usually effective at hundreds of meters, less often at up to a kilometer. At long distances in night conditions, it is difficult to detect a target if it does not emit light. A thermal imager is more suitable for such long-range observations.
Advantages and disadvantages of night vision devices and thermal imagers
Let's consider the strengths and weaknesses of each type of device. Below is a comparative summary based on expert data.
Advantages and disadvantages of night vision devices (NVD)
Advantages:
- High image detail. PNBs display objects as they are, but only in low light conditions. Newer generation devices provide a clear picture—you can distinguish faces, inscriptions, and small details. This is critical if you need to recognize a person or read a map in the dark.
- Natural perception of the scene. The image through the night vision device is close to what the eye sees in sufficient lighting (monochrome only). This makes it easier to navigate the terrain—you can see the relief, obstacles, and objects in their usual perspective. For example, when driving at night, soldiers use night vision goggles, which allow them to see the road and the surrounding terrain in its natural form.
- Effective operation in low light conditions. Even very faint light from stars or distant sources is sufficient for a high-quality PNB to form an image. With a third-generation device, you can observe on a moonless night—the starry sky and atmospheric glow often provide the necessary background. And with an IR illuminator, the PNB works even in complete darkness.
- Відносно невисока вартість. Класичні ПНБ і цифрові пристрої нічного бачення зазвичай дешевші за тепловізори аналогічного класу. Технологія підсилення видимого світла відпрацьована десятиліттями, виробництво ЕОП (особливо Gen 1–2) налагоджене, тому базові моделі доступні за ціною. Багато користувачів обирають ПНБ саме через бюджетні обмеження — нічні прилади можуть коштувати у кілька разів дешевше за тепловізори аналогічного призначення. Наприклад, найпростіший тепловізійний монокуляр обійдеться як два прилади нічного бачення 1-го покоління. Якщо бюджет обмежений — ПНБ часто є єдиним варіантом отримати пристрій для нічного полювання чи охорони.
Disadvantages:
- Complete darkness is the enemy of night vision devices. Without any external light (or without active IR illumination), a night vision device is useless. It cannot "see" anything if it is completely dark around it — this is a fundamental limitation of night vision devices. In addition, an IR illuminator, although invisible to the eye, can expose the observer if the enemy also has NVG.
- Чутливість до погодних умов. Для нормальної роботи ПНБ потрібен хоча б слабкий, але прямий огляд цілі. Дим, туман, пил або сильний дощ істотно погіршують якість зображення або роблять його неможливим. У густому тумані чи заметілі нічник стає безкорисним — світло розсіюється, не доходячи до приладу. Також у заростях чи за укриттями нерухому ціль із ПНБ можна просто не помітити. У таких випадках тепловізор, який бачить тепло крізь перешкоди, має величезну перевагу.
- The danger of bright light. Despite the presence of protection, flashes of bright light (e.g., headlights or explosions) can still temporarily blind the PNB user and overload the device's matrix. Older analog devices may even fail (burn out the image intensifier tube) when exposed to a sudden flash. Digital models are more reliable in this regard, but their sensitivity is also limited by the dynamic range of the sensor.
- Limited detection range. Although night vision devices allow you to see details better, the distance at which you can spot a target is limited by their ability to collect scattered light. Night vision devices are usually effective at hundreds of meters, less often at up to a kilometer. At long distances in night conditions, it is difficult to detect a target if it does not emit light. A thermal imager is more suitable for such long-range observations.
How EOP works: Gen2 and Gen3 generations
Щоб краще зрозуміти, чому прилади нічного бачення відрізняються за якістю та ціною, варто розібратися, як саме працює електронно-оптичний перетворювач (ЕОП) — головний елемент ПНБ. У статті пояснено еволюцію поколінь Gen2 → Gen3, вплив мікроканальної пластини, фотокатода, та різницю у світлочутливості між Photonis і американськими матрицями L3Harris.
Read the article about EOP Gen2 vs Gen3• різниця між поколіннями ЕОП • як формується зображення у темряві • порівняння технологій Photonis та L3Harris
How EOP works: Gen2 and Gen3 generations
Щоб краще зрозуміти, чому прилади нічного бачення відрізняються за якістю та ціною, варто розібратися, як саме працює електронно-оптичний перетворювач (ЕОП) — головний елемент ПНБ. У статті пояснено еволюцію поколінь Gen2 → Gen3, вплив мікроканальної пластини, фотокатода, та різницю у світлочутливості між Photonis і американськими матрицями L3Harris.
Read the article about EOP Gen2 vs Gen3• різниця між поколіннями ЕОП • як формується зображення у темряві • порівняння технологій Photonis та L3Harris
Advantages and disadvantages of thermal imagers
Advantages:
- Operates in complete darkness. Thermal imaging does not require any visible light, so it works in the middle of the night and in closed rooms without windows. You get images even where the eye (and night vision goggles) can see nothing. For example, a thermal imager allows you to observe the enemy in a dark forest without moonlight or detect a fugitive hiding in an abandoned basement.
- All-weather capability and penetration ability. Unlike IR cameras, thermal imagers remain effective in many challenging conditions: in fog, smoke, and through light vegetation. They can "see" through bushes and grass—a warm-blooded creature will reveal itself as a thermal silhouette. Even if the enemy is hidden behind a thin partition or thick foliage, their heat can still be detected. In bad weather (rain, snow), thermal imaging is often more effective: it registers the intrinsic radiation of objects, while night vision goggles suffer from a lack of visibility. Thus, thermal imaging is the #1 choice for detecting targets in conditions of zero visibility (night, smoke, cover).
- Long detection range. Thermal imagers are capable of detecting heat at long distances, significantly surpassing night vision devices in this parameter. For example, modern military thermal imagers can detect vehicles or people several kilometers away. Even civilian thermal imagers for hunting can detect large animals 1.5–2 km away. Thermal contrast is often visible before the object can be seen through optics, which is a big plus for perimeter security and reconnaissance.
- Independence from the time of day. With a thermal imager, you can observe equally successfully during the day and at night. It also works during the day, although strong solar heating can slightly reduce contrast. However, it is not "blinded" by the sun — you can even look against the sunset and see the thermal silhouette of the target. At night, thermal imaging has virtually no competition in terms of continuous operation: the transitional twilight period is not a problem for it (unlike night vision goggles, which are affected by twilight). Therefore, thermal imaging is a universal 24/7 surveillance tool for security posts or patrols.
Disadvantages:
- Limited detail and recognition. A thermal imager is great at detecting objects, but it doesn't give you clear details—you can only see outlines and temperature distribution on the screen. It's impossible to recognize faces or writing, or to tell if someone is a friend or foe. For accurate identification, you usually need a night vision device.
- Dependence on thermal contrast and environmental conditions. In hot weather, after sunset, or during rain and wet snow, the thermal contrast between the object and the background decreases, making detection more difficult. Thermal imaging cameras also cannot "see" through glass, thick fog, or water surfaces.
- Higher energy consumption and weight. Large germanium lenses make the device heavier, and the electronics consume more energy, so the battery life is shorter than that of an LED flashlight. Spare batteries are required for long missions.
- Need for user experience. Interpreting thermal images requires practice: artifacts, glare, or residual heat can create false signals. Without experience, the operator may confuse background heat sources with the actual target.
- The price depends on the level of technology. Inexpensive thermal imagers are already available, but models with high resolution, long-focus optics, and features such as rangefinders or ballistic calculators remain expensive. In the mid-range and premium classes, night vision devices and thermal imagers cost about the same but perform different tasks.
Advantages and disadvantages of thermal imagers
Advantages:
- Operates in complete darkness. Thermal imaging does not require any visible light, so it works in the middle of the night and in closed rooms without windows. You get images even where the eye (and night vision goggles) can see nothing. For example, a thermal imager allows you to observe the enemy in a dark forest without moonlight or detect a fugitive hiding in an abandoned basement.
- All-weather capability and penetration ability. Unlike IR cameras, thermal imagers remain effective in many challenging conditions: in fog, smoke, and through light vegetation. They can "see" through bushes and grass—a warm-blooded creature will reveal itself as a thermal silhouette. Even if the enemy is hidden behind a thin partition or thick foliage, their heat can still be detected. In bad weather (rain, snow), thermal imaging is often more effective: it registers the intrinsic radiation of objects, while night vision goggles suffer from a lack of visibility. Thus, thermal imaging is the #1 choice for detecting targets in conditions of zero visibility (night, smoke, cover).
- Long detection range. Thermal imagers are capable of detecting heat at long distances, significantly surpassing night vision devices in this parameter. For example, modern military thermal imagers can detect vehicles or people several kilometers away. Even civilian thermal imagers for hunting can detect large animals 1.5–2 km away. Thermal contrast is often visible before the object can be seen through optics, which is a big plus for perimeter security and reconnaissance.
- Independence from the time of day. With a thermal imager, you can observe equally successfully during the day and at night. It also works during the day, although strong solar heating can slightly reduce contrast. However, it is not "blinded" by the sun — you can even look against the sunset and see the thermal silhouette of the target. At night, thermal imaging has virtually no competition in terms of continuous operation: the transitional twilight period is not a problem for it (unlike night vision goggles, which are affected by twilight). Therefore, thermal imaging is a universal 24/7 surveillance tool for security posts or patrols.
Disadvantages:
- Limited detail and recognition. A thermal imager is great at detecting objects, but it doesn't give you clear details—you can only see outlines and temperature distribution on the screen. It's impossible to recognize faces or writing, or to tell if someone is a friend or foe. For accurate identification, you usually need a night vision device.
- Dependence on thermal contrast and environmental conditions. In hot weather, after sunset, or during rain and wet snow, the thermal contrast between the object and the background decreases, making detection more difficult. Thermal imaging cameras also cannot "see" through glass, thick fog, or water surfaces.
- Higher energy consumption and weight. Large germanium lenses make the device heavier, and the electronics consume more energy, so the battery life is shorter than that of an LED flashlight. Spare batteries are required for long missions.
- Need for user experience. Interpreting thermal images requires practice: artifacts, glare, or residual heat can create false signals. Without experience, the operator may confuse background heat sources with the actual target.
- The price depends on the level of technology. Inexpensive thermal imagers are already available, but models with high resolution, long-focus optics, and features such as rangefinders or ballistic calculators remain expensive. In the mid-range and premium classes, night vision devices and thermal imagers cost about the same but perform different tasks.
Monocular or binocular: what to choose for night vision?
Після того як ви розібралися з технологіями нічного бачення і принципом роботи ЕОП, варто визначитися з форм-фактором. У цій статті розглянуто відмінності між монокуляром (легкість, універсальність) та бінокуляром (стереозір, зручність спостереження), а також вплив ширококутних систем 50–97° на ситуаційну обізнаність.
Go to comparison• польова ергономіка та баланс шолома • вплив кута огляду на SA • практичні поради з вибору кріплення та контрваги
Monocular or binocular: what to choose for night vision?
Після того як ви розібралися з технологіями нічного бачення і принципом роботи ЕОП, варто визначитися з форм-фактором. У цій статті розглянуто відмінності між монокуляром (легкість, універсальність) та бінокуляром (стереозір, зручність спостереження), а також вплив ширококутних систем 50–97° на ситуаційну обізнаність.
Go to comparison• польова ергономіка та баланс шолома • вплив кута огляду на SA • практичні поради з вибору кріплення та контрваги
What to choose: a thermal imager or a night vision device?
Як ми побачили, тепловізори та прилади нічного бачення (ПНБ) не є взаємозамінними — кожен із них має свої сильні й слабкі сторони. В ідеалі ці пристрої доповнюють один одного, а вибір залежить від завдань користувача. Експерти сходяться на думці, що не існує однозначно кращого варіанту «на всі випадки». Тому, вирішуючи, що придбати, враховуйте умови застосування.
Here are some recommendations based on the experience of military personnel and hunters:
- A thermal imager is best suited for detecting targets in difficult conditions (complete darkness, dense vegetation, camouflaged enemies). It ensures that you will notice the heat of the target, even if it blends in with the background in color or remains motionless. For example, a thermal imager is indispensable for an observer at a checkpoint—it allows you to see a sneaking intruder at night or in fog, when a regular camera is powerless. When hunting, a thermal imager will help you quickly find an animal in tall grass or determine the location of wounded game by its heat signature.
- Для розпізнавання, прицілювання та керування технікою доцільніше використовувати ПНБ. Якщо ваше завдання — ідентифікувати об’єкт, розрізнити його деталі (спорядження, жести, номери техніки тощо), прилад нічного бачення забезпечить чіткішу картинку. Тому бійці часто застосовують ПНБ для безпосереднього спостереження під час спеціальних операцій: з його допомогою можна тихо вести розвідку, помітити дротяні розтяжки, безпечно пересуватися без фар у складному рельєфі. ПНБ також зручніші для прицілювання, коли ціль перебуває у зоні видимості — нічний приціл чітко покаже перехрестя та об’єкт. На цивільному ринку мисливці обирають ПНБ, бажаючи отримати більш «живе» зображення трофея і можливість знімати відео з деталями оточення.
- Consider distance and terrain. Open spaces (fields, steppes) at long distances are an advantage for thermal imaging, as it will detect movement or heat earlier than an IR night vision device. In urban environments or indoors, where there are many shelters and obstacles, night vision goggles or a combination of the two devices work better. If you need to monitor the situation at close range (up to 100–200 m) and it is important to recognize people, choose night vision goggles. For long-range observation or perimeter security of a large area, it is advisable to have a thermal imager.
- Бюджет і доступність. Оцініть, скільки коштів ви готові витратити. Обмежений бюджет часто схиляє вибір на користь приладів нічного бачення — серед них більше недорогих моделей, особливо цифрових або старіших поколінь, які при цьому виконують основні функції. Недорогі тепловізори часто мають меншу роздільну здатність і дальність, тому можуть поступатися якісному ПНБ за деталізацією. Якщо бюджет дозволяє, оптимально використовувати комбінацію: як зазначають фахівці, нічний приціл + тепловізійний монокуляр дають найкращий результат. Монокуляром зручно сканувати територію, а через ПНБ-приціл — розглядати ціль і, за потреби, діяти точно. Такий підхід активно застосовують мисливці й військові.
- Combat conditions and safety. In the realities of modern warfare (particularly in Ukraine), both technologies are so important that the question of "which is better" is irrelevant—both types of devices are needed. Night vision goggles enable soldiers to move and operate effectively in the dark, serving as their "eyes" at night, while thermal imaging devices are a means of reconnaissance and detection of enemies hiding in cover or camouflage. That is why military units try to have both types of optics. When it comes to volunteers or civilians who help the army, priority is often given to thermal imagers — they significantly increase the ability to detect the enemy in positional warfare. At the same time, night vision goggles remain in demand — for example, for drivers, armored vehicle mechanics, sappers, etc.
Conclusion:
Обираючи між тепловізором і приладом нічного бачення, спочатку чітко визначте свої цілі та умови використання. Якщо вам потрібна чітка картинка і розпізнавання — обирайте ПНБ. Якщо критично важливо помітити будь-який рух або джерело тепла на максимальній відстані — ваш вибір тепловізор. Ідеальний варіант — мати обидва прилади та використовувати кожен за призначенням.
As experienced hunters and military personnel say: "At night, a thermal imager will help you detect a target, and a night vision device will help you identify it." Practice shows that combining these technologies gives the best results. If you still have doubts, consult with specialists: experts in optical devices will advise you on the best solution for your specific tasks.
Remember: both thermal imaging cameras and night vision goggles significantly expand your capabilities at night, increasing the effectiveness and safety of your actions. Use them wisely, and darkness will no longer be an obstacle.
What to choose: a thermal imager or a night vision device?
Як ми побачили, тепловізори та прилади нічного бачення (ПНБ) не є взаємозамінними — кожен із них має свої сильні й слабкі сторони. В ідеалі ці пристрої доповнюють один одного, а вибір залежить від завдань користувача. Експерти сходяться на думці, що не існує однозначно кращого варіанту «на всі випадки». Тому, вирішуючи, що придбати, враховуйте умови застосування.
Here are some recommendations based on the experience of military personnel and hunters:
- A thermal imager is best suited for detecting targets in difficult conditions (complete darkness, dense vegetation, camouflaged enemies). It ensures that you will notice the heat of the target, even if it blends in with the background in color or remains motionless. For example, a thermal imager is indispensable for an observer at a checkpoint—it allows you to see a sneaking intruder at night or in fog, when a regular camera is powerless. When hunting, a thermal imager will help you quickly find an animal in tall grass or determine the location of wounded game by its heat signature.
- Для розпізнавання, прицілювання та керування технікою доцільніше використовувати ПНБ. Якщо ваше завдання — ідентифікувати об’єкт, розрізнити його деталі (спорядження, жести, номери техніки тощо), прилад нічного бачення забезпечить чіткішу картинку. Тому бійці часто застосовують ПНБ для безпосереднього спостереження під час спеціальних операцій: з його допомогою можна тихо вести розвідку, помітити дротяні розтяжки, безпечно пересуватися без фар у складному рельєфі. ПНБ також зручніші для прицілювання, коли ціль перебуває у зоні видимості — нічний приціл чітко покаже перехрестя та об’єкт. На цивільному ринку мисливці обирають ПНБ, бажаючи отримати більш «живе» зображення трофея і можливість знімати відео з деталями оточення.
- Consider distance and terrain. Open spaces (fields, steppes) at long distances are an advantage for thermal imaging, as it will detect movement or heat earlier than an IR night vision device. In urban environments or indoors, where there are many shelters and obstacles, night vision goggles or a combination of the two devices work better. If you need to monitor the situation at close range (up to 100–200 m) and it is important to recognize people, choose night vision goggles. For long-range observation or perimeter security of a large area, it is advisable to have a thermal imager.
- Бюджет і доступність. Оцініть, скільки коштів ви готові витратити. Обмежений бюджет часто схиляє вибір на користь приладів нічного бачення — серед них більше недорогих моделей, особливо цифрових або старіших поколінь, які при цьому виконують основні функції. Недорогі тепловізори часто мають меншу роздільну здатність і дальність, тому можуть поступатися якісному ПНБ за деталізацією. Якщо бюджет дозволяє, оптимально використовувати комбінацію: як зазначають фахівці, нічний приціл + тепловізійний монокуляр дають найкращий результат. Монокуляром зручно сканувати територію, а через ПНБ-приціл — розглядати ціль і, за потреби, діяти точно. Такий підхід активно застосовують мисливці й військові.
- Combat conditions and safety. In the realities of modern warfare (particularly in Ukraine), both technologies are so important that the question of "which is better" is irrelevant—both types of devices are needed. Night vision goggles enable soldiers to move and operate effectively in the dark, serving as their "eyes" at night, while thermal imaging devices are a means of reconnaissance and detection of enemies hiding in cover or camouflage. That is why military units try to have both types of optics. When it comes to volunteers or civilians who help the army, priority is often given to thermal imagers — they significantly increase the ability to detect the enemy in positional warfare. At the same time, night vision goggles remain in demand — for example, for drivers, armored vehicle mechanics, sappers, etc.
Conclusion:
Обираючи між тепловізором і приладом нічного бачення, спочатку чітко визначте свої цілі та умови використання. Якщо вам потрібна чітка картинка і розпізнавання — обирайте ПНБ. Якщо критично важливо помітити будь-який рух або джерело тепла на максимальній відстані — ваш вибір тепловізор. Ідеальний варіант — мати обидва прилади та використовувати кожен за призначенням.
As experienced hunters and military personnel say: "At night, a thermal imager will help you detect a target, and a night vision device will help you identify it." Practice shows that combining these technologies gives the best results. If you still have doubts, consult with specialists: experts in optical devices will advise you on the best solution for your specific tasks.
Remember: both thermal imaging cameras and night vision goggles significantly expand your capabilities at night, increasing the effectiveness and safety of your actions. Use them wisely, and darkness will no longer be an obstacle.
More about thermal imaging and night vision: technologies, principles, practice
A selection of verified sources for a deeper understanding of the topic — from the principles of thermal imaging and PNB to modern research and examples of practical application.
- What’s the Difference between Thermal Imaging and Night Vision? — FLIR Systems (an accessible explanation of the difference between thermal imaging and night vision optics: how they work, their advantages and limitations).
- Infrared Thermal Imaging Night Vision System — GST Infrared (overview of infrared thermography applications in night vision systems, sensor types, operating conditions).
- Facts and FAQs about Thermal Imaging — Mongabay (базові принципи тепловізійної технології, типові сфери використання та фізичні обмеження).
- Night Vision Techniques (PDF) — Academia .edu (scientific review of night vision and thermal imaging methods, evolution of generations, and directions for development).
- Review on Infrared Imaging Technology — MDPI Sustainability Journal (current overview of infrared technology, its use in surveillance, energy, and security).
More about thermal imaging and night vision: technologies, principles, practice
A selection of verified sources for a deeper understanding of the topic — from the principles of thermal imaging and PNB to modern research and examples of practical application.
- What’s the Difference between Thermal Imaging and Night Vision? — FLIR Systems (an accessible explanation of the difference between thermal imaging and night vision optics: how they work, their advantages and limitations).
- Infrared Thermal Imaging Night Vision System — GST Infrared (overview of infrared thermography applications in night vision systems, sensor types, operating conditions).
- Facts and FAQs about Thermal Imaging — Mongabay (базові принципи тепловізійної технології, типові сфери використання та фізичні обмеження).
- Night Vision Techniques (PDF) — Academia .edu (scientific review of night vision and thermal imaging methods, evolution of generations, and directions for development).
- Review on Infrared Imaging Technology — MDPI Sustainability Journal (current overview of infrared technology, its use in surveillance, energy, and security).



Thermal imager or night vision device – which is better? A complete comparison and advice